How to Choose a Sleeper Sofa: Comfort, Mechanisms, and Space-Saving Tips
Why Sleeper Sofas Matter + Outline
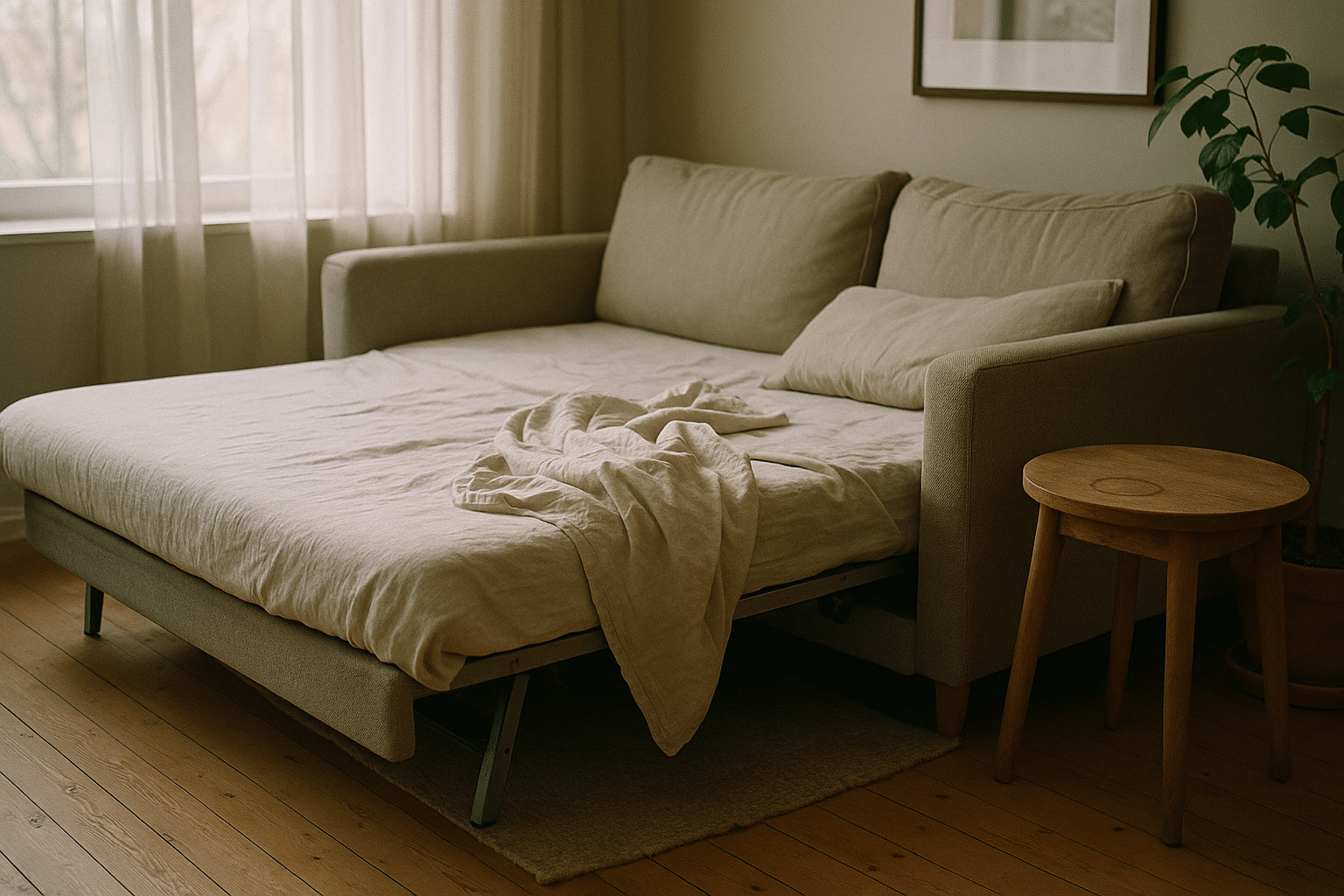
A sleeper sofa has a big job: it must sit comfortably by day, sleep reliably by night, and fit a room that may already be working overtime as an office, den, or studio. That means you’re weighing seat ergonomics, mattress support, and the choreography of opening and closing a bed without scraping knuckles or blocking doors. Done right, the sleeper you choose extends hospitality without sacrificing everyday comfort. Done hastily, it becomes a creaky compromise that eats space and leaves guests stiff. This guide lays out the key choices, translates jargon into plain language, and gives you a decision path that matches your room, routines, and budget.
Outline of what you’ll find below:
– Comfort science: mattress materials, cushion densities, and how sleeper design affects your spine and pressure points.
– Mechanisms compared: pull-out, click-clack, futon, pop-up/lift-and-slide, and sectional hybrids, with realistic pros and cons.
– Space strategy: measurement methods, doorway math, open-clearance planning, and storage tricks that actually work.
– Build quality: frames, suspensions, fabrics, and long-term maintenance that keeps squeaks and sags at bay.
– Buying checklist and conclusion: a step-by-step path to a confident purchase, plus upkeep tips for years of use.
As you read, keep your primary use in mind. If guests stay a few times a year, you might prioritize lounge comfort and a fast, quiet mechanism. If it doubles as a nightly sleeper for a studio, durable support and breathable materials take the lead. Useful rule of thumb: the more often it’s used for sleeping, the more you should scrutinize mattress thickness, support layers, and how the mechanism distributes weight. By the end, you’ll have a short list that fits your floor plan and your lifestyle, not someone else’s showroom script.
Comfort Science: Mattress Types, Cushioning, and Sleep Ergonomics
Comfort starts with the sleep surface, and sleeper sofas use compact systems designed to fold, slide, or compress. The usual suspects are memory foam, latex, innerspring, or a hybrid that stacks foam over coils or a webbed deck. Each handles pressure, heat, and motion differently. Memory foam conforms well and can reduce pressure on shoulders and hips, but lower-density foams may trap heat and lose resilience faster. Latex tends to feel springier, is naturally breathable, and often outlasts poly foams, though it can feel buoyant if you prefer a slow, “hugging” sink. Innersprings offer airflow and edge stability; however, thin mattresses over firm decks can reveal that infamous “bar-in-the-back” feeling unless the mechanism includes improved decking or a topper layer. Hybrids aim to balance contouring and support while keeping foldability manageable.
Thickness matters. Many sleeper mattresses range from about 4 to 6 inches. At 4 inches, foam quality and the support platform underneath become critical. Look for high-resilience foam in the 1.8–2.5 lb/ft³ range for core layers, with softer comfort foam or latex above to spread pressure. Side sleepers usually appreciate a slightly plusher top layer; back sleepers may prefer firmer, even support with less hip sink. If you’re testing in person, lie diagonally to check shoulder room, and note whether your pelvis feels aligned or tipped. If ordering online, seek specs beyond vague terms like “plush” or “supportive.” Numbers to watch include foam density (lb/ft³), indentation load deflection (ILD) for latex or foam firmness, and fabric breathability features such as knit covers or ventilated cores.
Seating comfort is just as important because you’ll sit on this more than you’ll sleep on it. Cushion cores with 1.8–2.2 lb/ft³ foam are common for sofas; higher-density or wrapped spring cushions can maintain shape longer. Seat height around 17–19 inches suits most adults, and a seat depth of 20–24 inches can balance upright posture with lounging. Suspension under the seat—sinuous springs or strong webbing—helps eliminate “hammocking” over time. Small details add up:
– A breathable cover reduces heat build-up during sleep.
– Tapered arms or bolsters can serve as adjustable pillows for lounging.
– A smooth deck under the mattress reduces pressure points you might otherwise feel as a ridge or bar.
If two people will share the sleeper frequently, consider motion isolation. Foams generally dampen movement, while bouncy support layers can transfer it. Also factor in temperature: hot sleepers often do better with latex or aerated foams and moisture-wicking covers. Above all, prioritize alignment. A sleeper that keeps your spine neutral will feel more restorative in the morning than a thicker pad that lets hips sink out of line.
Understanding Mechanisms: Pull-Outs, Click-Clacks, Futons, and Hybrids
The mechanism is the sleeper’s engine. It determines how the bed deploys, whether the mattress is separate from the seat cushions, and how easy it is to operate in tight quarters. Classic pull-out designs hide a folded mattress under the seat; you remove cushions, pull a handle, and unfold a bi- or tri-fold frame. A well-designed pull-out spreads weight with webbing or fabric decking, which minimizes the sensation of crossbars and reduces squeak points. Pros: familiar feel, mattress choices, and clear separation between seating foam and sleep surface. Cons: more moving parts, heavier frames, and the need to stash cushions when converting.
Click-clack mechanisms pivot the backrest; you push the back forward slightly and then let it drop flat. Pros: fast conversion, one-piece sleep surface, fewer parts to fail. Cons: the seam where seat meets back can be felt, and the flat plane may not contour like a dedicated mattress. Futon-style frames—typically a bi-fold platform—offer simple engineering with slats or a solid deck and a single mattress pad. Pros: affordable, durable, and easy to service or replace the mattress. Cons: comfort depends heavily on the futon pad quality and slat spacing, and the seat may feel firmer than a traditional sofa. Lift-and-slide or pop-up designs hide a trundle-like platform under the seat that rises flush with the main cushions. Pros: minimal lifting effort and no cushion removal. Cons: thinner sleep layers and potential height mismatch if not engineered precisely.
Sectional hybrids sometimes combine a pop-up platform with a chaise, creating a larger sleeping area when extended. These are appealing for family rooms because they turn into a lounge-friendly “island” by day. When comparing mechanisms, test the cycle: unlatch, pull, pivot, and lock. Listen for grinding or scraping. Look for evenly welded joints, coated or plated steel components to reduce corrosion, and secure pivot fasteners. Many mechanisms are rated for thousands of open/close cycles; while exact ratings vary, selecting a design that feels smooth and locks positively will pay off in durability. Consider your space and habits:
– Frequent guests: a mechanism you can open with one hand, quietly, in under a minute.
– Tight rooms: a click-clack or pop-up that keeps the footprint compact.
– Sensitive sleepers: a pull-out or hybrid with upgraded decking and a distinct mattress.
Noise is another differentiator. A little initial stiffness can be normal, but persistent squeaks signal friction points. A light application of dry silicone to recommended contact surfaces (check manufacturer guidance) helps. If you anticipate daily conversions, lighter mechanisms with fewer steps will save time and reduce wear, whereas a weekly guest bed can justify a heavier pull-out with a thicker, more supportive mattress.
Space-Saving and Measurement Mastery
Space planning makes or breaks sleeper ownership. Begin with two sets of measurements: closed dimensions and open-bed dimensions. Most sleepers list width (arm to arm), depth, and overall height, plus the length when opened. As a starting range, plan for roughly 90–95 inches of overall length when a queen-size pull-out opens; 85–90 inches for full; and 75–80 inches for twin, though exact numbers vary by design. Leave at least 24–30 inches of clearance at the foot for getting in and out; 36 inches is more comfortable for high-traffic rooms. If a coffee table must stay, choose one that slides easily or nests to one side. Mark the footprint with painter’s tape on the floor and rehearse the motion—pretend to open, walk around, and sit—to see what collides.
Delivery paths matter as much as the destination. Measure door widths, hallway turns, stair landings, and elevator cabins. For doors, note the clear opening—the space between stops—rather than the door panel size. If a model allows removing legs or arms, that can shave precious inches, but confirm the process and required tools. When in doubt, measure the diagonal depth of the sofa (from the top back corner to the front-bottom corner) and compare with hallway diagonals; this helps predict whether a pivot turn is possible. Protect floors with felt pads under legs and ensure rugs are either heavy enough not to bunch or easy to slide aside before opening the bed.
To keep small rooms flexible:
– Choose arms that are slim to reclaim width without sacrificing seating.
– Consider storage ottomans for bedding and pillows to avoid clutter.
– If your room has a bay window or alcove, a pop-up mechanism may open forward without hitting walls.
– Wall clearance of 2–3 inches behind the sofa allows airflow and prevents scuffs during minor shifts.
Think vertical, too. Tall backs can crowd windowsills or art; low-profile backs keep sightlines open and make rooms feel larger. Upholstery color affects perceived size—lighter, low-contrast tones visually recede, while bold colors become focal points. Finally, map outlets and lighting. You’ll want a reachable lamp or sconce for nighttime reading and a surface for a glass of water that won’t block the opening path. With careful measurement and a few dry runs, your sleeper can transform on cue without drama.
Buying Checklist and Conclusion: Bringing It All Home
Turn research into a confident choice with a clear checklist. Start by writing your primary use: occasional guests, frequent guests, or nightly sleeping. Then set non-negotiables: maximum width, open length, and minimum clearance needed for walking. Decide on comfort priorities—cooler sleep, motion isolation, or a contouring feel. Shortlist mechanisms that fit your room and routine. If possible, test in person: sit for 10 minutes, lie down for 5, and open/close the bed twice while noting noise and effort. Ask for specifications beyond generic labels:
– Mattress: thickness in inches, foam density (lb/ft³), and whether there’s a ventilated or webbed deck.
– Seating: cushion density or spring wrap, seat height, and suspension type (sinuous vs webbing).
– Frame: hardwood or engineered plywood rails, joint reinforcement, and metal gauge on moving parts.
Plan for longevity. Look for replaceable components—bolt-on legs, removable backrests, or a swappable mattress—so you can refresh without replacing the whole piece. Fabric matters for wear and upkeep; tightly woven synthetics and performance finishes can resist stains, while natural fibers breathe but may need gentler care. Check care codes on upholstery: W (water-based cleaners), S (solvent), WS (either), or X (vacuum only). Maintenance is simple but effective: vacuum crevices monthly, tighten accessible bolts every six months, and inspect hinges for looseness or rub points. A light, manufacturer-approved dry lubricant on pivots can tame squeaks. Rotate or flip the mattress if the design allows; even rotations every few months can even out wear.
Budget by total value, not sticker alone. Consider frequency of use and the potential to replace a guest bed, daybed, or air mattress. A well-constructed sleeper can consolidate furniture and free floor space, which is especially meaningful in small homes. Delivery and assembly are part of the equation—measure the path, schedule adequate time, and keep basic tools on hand. If buying online, read return and exchange policies carefully; large items may carry restocking or pickup fees. In shared homes, agree on upholstery color and texture in advance to avoid post-delivery surprises.
Conclusion: A sleeper sofa is a quiet workhorse, turning square footage into flexible comfort without fanfare. Match the mechanism to your daily rhythm, choose materials that support real bodies for real sleep, and measure like a pro. With a clear checklist and a room-aware plan, you’ll welcome guests easily, lounge comfortably every day, and keep your living space calm, useful, and ready for whatever the week brings.